By Stacy Levy
The Schuylkill Center for Environmental Education is working to investigate the intersection of nature and the city. The role of rain in the landscape is being actively explored in programs and planning around its buildings. As a nature center, SCEE is at the forefront of solving site issues through art based intervention. On May 31, 2013 a conference on New Environmental Art will be held at SCEE to look at ways that art and science can collaborate to solve ecological problems in urban nature, and enlighten citizens to find new solutions in their own lives.
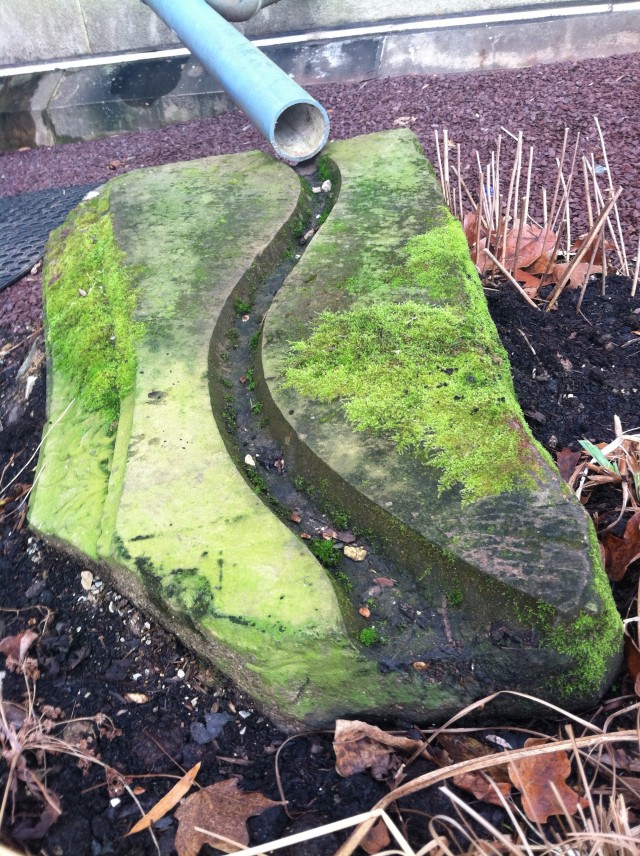

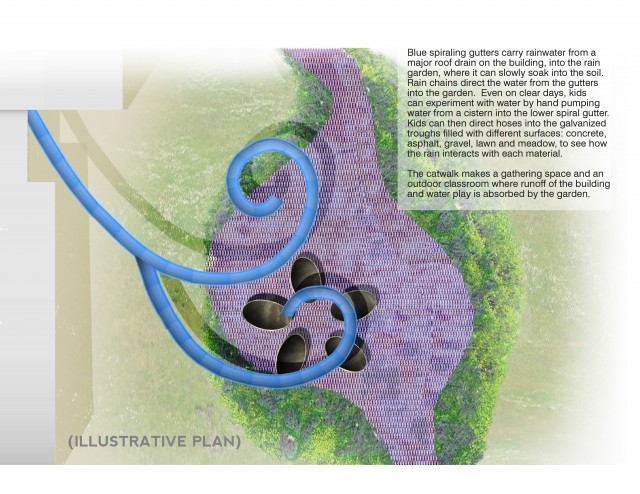
Give people a more narrow path of movement around a site while rain gets plenty of space to spread out and linger? How would our built environments change? And how would it change our relationship to rain?As an eco-artist, I want art to be an advocate of rain. Art is good at giving meaning to the leftover or abandoned aspects of the world—and rain is one of those abandoned elements. Though a yardstick worth of rain falls every yearin this region, we hardly register rain’s presence. In urban settings, architecture and engineering have generally kept rain invisible to us. The relationship between rain and the built environment needs to be changed, and art is well positioned to alter that relationship.At SCEE, I am working with ecologists, engineers and educators to create an artwork that gives the rain room to spread out while keeping people in a defined space. But people do not lose out in this design— both rain and visitors get a dynamic space to co-exist.Rain Gardens create spaces that can get wet and stay wet while the water infiltrates into the soil.
Instead of becoming a muddy soup, the rain garden holds the rain within the permeable soil and the roots of a diverse community of native plants . These plants also make good habitat for other species like insects and food for birds and other small mammals.
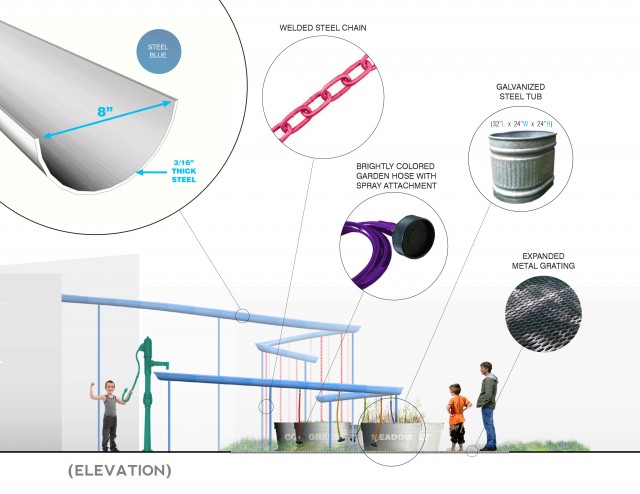
This new artwork deals with two types of visitors to the site: rain and humans. A grated metal catwalk prevents the plants from being trampled while also keeping people’s feet dry. ‘Staying dry’ and ‘soaking in’ are two incongruent activities—one of the reasons that rain has no place to go in the built world is the hierarchy of the dry human foot!
We want to demonstrate ways to change rain’s journey in the built environment. We also want to give visitors a chance to test out the very materials of the city: the surfaces we spend our lives walking on like asphalt, concrete and grass. How do these materials work with or work against rain?
How this art works: Some of the rainwater will be diverted and stored in an above ground cistern. Then during dry days, our visitors can pump this contained water into 5 different troughs. Each trough contains a different familiar surface materials from the landscape: concrete, asphalt, gravel lawn and meadow. People can direct the rainwater onto these different surfaces to see how the water responds— by soaking in or running off.
At SCEE rainwater will be given both the time and the place to act the way rain should act. And people will be given a place to interact with the falling rain while staying out of its way as it soaks into the soil. The idea of rain needing a refuge is a new idea to most of us. We hope people learn about rain, and the surfaces it meets in our world. This piece gives people a new angle on rain and its relationship to our built environment.
The piece will be under construction over the early spring. Please come by and see it!
Want to know more about Rain Gardens?
The Philadelphia Water Department
The Department of Environmental Conservation
©2012 Stacy Levy